- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Emergency and disaster management training; knowledge and attitude of Yemeni health professionals- a cross-sectional study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Medical professionals together with other first responder teams are the first to attend an emergency or disaster. Knowledge and training in emergency and disaster preparedness are important in responding effectively.
This study aims to assess the current knowledge, attitude and training in emergency and disaster preparedness among Yemeni health professionals.
Method
A descriptive, cross-sectional, non-probability based study was conducted in Yemen using self-reported on-line and paper surveys in 2017. A total of 531 health professionals responded. The Chi-Square test was used to identify any significant difference in the knowledge and attitude of the professional categories. The p-value of <0.05 was used as a statistical significant.
Results
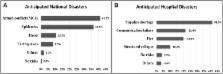
The overall knowledge status of Yemeni health professionals was insufficient with regards to emergency and disaster preparedness. Of all respondents, 32.0% had good knowledge, 53.5% had fair and 14.5% exhibited poor knowledge. The educational level was a key factor in the knowledge gap amongst respondents. Regardless of the period of experience, postgraduate staff were more knowledgeable than graduates. Physicians were better in knowledge than other subgroups of health specialties. Health administrators seemed insufficiently qualified in emergency and disaster planning. Medical teachers performed better in responding to knowledge test than managers. However, the majority of study respondents appeared in the ‘positive attitudes’ level to emergency and disaster preparedness. 41.0% of all respondents had received no courses in disaster preparedness. The trained staff used NGOs, and online-related programs more frequently for learning disaster planning (15.7%, and 13.6%) respectively. In contrast, formal resources such as MoPHP, health facility, medical schooling programs were used by (10.2%, 9.6, and 7.3%) of respondents, respectively. 58.9% of respondents had not participated in any exercise in emergency and disaster preparedness. Of all respondents, triage and mass causality response exercises were attended by only (13.5%, and 9.7%) respectively.
Conclusion
The absence of teaching programs is a major issue in the lack of knowledge of health professionals regarding disaster preparedness. Thus, emergency and disaster preparedness has to be included in the primary medical school curricula and continuing medical education programs of the health facilities. Long-term formal training such as undergraduate and postgraduate programs is necessary. Operational simulations enrolled key personnel of multi-agencies focus on an organizational training rather than individual based training are recommended.
Related collections
Most cited references16

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Resilience in the Face of Disaster: Prevalence and Longitudinal Course of Mental Disorders following Hurricane Ike

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Mental Health Problems among the Survivors in the Hard-Hit Areas of the Yushu Earthquake

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found