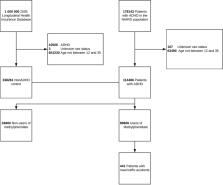
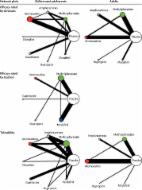
Summary Background The benefits and safety of medications for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) remain controversial, and guidelines are inconsistent on which medications are preferred across different age groups. We aimed to estimate the comparative efficacy and tolerability of oral medications for ADHD in children, adolescents, and adults. Methods We did a literature search for published and unpublished double-blind randomised controlled trials comparing amphetamines (including lisdexamfetamine), atomoxetine, bupropion, clonidine, guanfacine, methylphenidate, and modafinil with each other or placebo. We systematically contacted study authors and drug manufacturers for additional information. Primary outcomes were efficacy (change in severity of ADHD core symptoms based on teachers' and clinicians' ratings) and tolerability (proportion of patients who dropped out of studies because of side-effects) at timepoints closest to 12 weeks, 26 weeks, and 52 weeks. We estimated summary odds ratios (ORs) and standardised mean differences (SMDs) using pairwise and network meta-analysis with random effects. We assessed the risk of bias of individual studies with the Cochrane risk of bias tool and confidence of estimates with the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation approach for network meta-analyses. This study is registered with PROSPERO, number CRD42014008976. Findings 133 double-blind randomised controlled trials (81 in children and adolescents, 51 in adults, and one in both) were included. The analysis of efficacy closest to 12 weeks was based on 10 068 children and adolescents and 8131 adults; the analysis of tolerability was based on 11 018 children and adolescents and 5362 adults. The confidence of estimates varied from high or moderate (for some comparisons) to low or very low (for most indirect comparisons). For ADHD core symptoms rated by clinicians in children and adolescents closest to 12 weeks, all included drugs were superior to placebo (eg, SMD −1·02, 95% CI −1·19 to −0·85 for amphetamines, −0·78, −0·93 to −0·62 for methylphenidate, −0·56, −0·66 to −0·45 for atomoxetine). By contrast, for available comparisons based on teachers' ratings, only methylphenidate (SMD −0·82, 95% CI −1·16 to −0·48) and modafinil (−0·76, −1·15 to −0·37) were more efficacious than placebo. In adults (clinicians' ratings), amphetamines (SMD −0·79, 95% CI −0·99 to −0·58), methylphenidate (−0·49, −0·64 to −0·35), bupropion (−0·46, −0·85 to −0·07), and atomoxetine (−0·45, −0·58 to −0·32), but not modafinil (0·16, −0·28 to 0·59), were better than placebo. With respect to tolerability, amphetamines were inferior to placebo in both children and adolescents (odds ratio [OR] 2·30, 95% CI 1·36–3·89) and adults (3·26, 1·54–6·92); guanfacine was inferior to placebo in children and adolescents only (2·64, 1·20–5·81); and atomoxetine (2·33, 1·28–4·25), methylphenidate (2·39, 1·40–4·08), and modafinil (4·01, 1·42–11·33) were less well tolerated than placebo in adults only. In head-to-head comparisons, only differences in efficacy (clinicians' ratings) were found, favouring amphetamines over modafinil, atomoxetine, and methylphenidate in both children and adolescents (SMDs −0·46 to −0·24) and adults (−0·94 to −0·29). We did not find sufficient data for the 26-week and 52-week timepoints. Interpretation Our findings represent the most comprehensive available evidence base to inform patients, families, clinicians, guideline developers, and policymakers on the choice of ADHD medications across age groups. Taking into account both efficacy and safety, evidence from this meta-analysis supports methylphenidate in children and adolescents, and amphetamines in adults, as preferred first-choice medications for the short-term treatment of ADHD. New research should be funded urgently to assess long-term effects of these drugs. Funding Stichting Eunethydis (European Network for Hyperkinetic Disorders), and the UK National Institute for Health Research Oxford Health Biomedical Research Centre.