- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Natural Extracts as Inhibitors of Microorganisms and Lipid Oxidation in Emulsion Sausage during Storage
Read this article at
Abstract
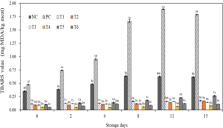
Food additives are required to maintain the freshness and quality of foods, particularly meats. However, chemical additives may not be preferred by consumers, and natural materials with antimicrobial and antioxidant effects may be used as replacements for common chemical additives. Accordingly, in this study, we compared the antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of natural compounds extracted with ethanol and hot water, and emulsion sausage prepared with natural ethanol extracts was analyzed for pH, color, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), and Clostridium perfringens growth during storage. The antimicrobial activities of 49 natural extract candidates against Listeria monocytogenes, C. perfringens , Salmonella spp., and Escherichia coli were analyzed, and six natural materials with excellent antibacterial activities, i.e., Elaeagnus umbellata Thunb. f. nakaiana (Araki) H. Ohba, Punica granatum L., Ecklonia cava, Nelumbo nucifera Gaertner, and Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill., and Rubus coreanus Miq. were evaluated to determine their total polyphenol contents and DPPH radical scavenging activities. The total polyphenol contents of ethanol extracts were higher than those of hot water extracts, whereas DPPH radical scavenging activity was found to be higher in hot water extracts. The TBARS values of emulsion sausages were significantly increased as storage time increased, and the TBARS values of emulsion sausages prepared with natural extracts were lower than those of control sausages. Natural extract-treated emulsion sausages showed a 99% reduction in bacterial contents compared with untreated sausages on day 2, with greater than 99.9% reduction after day 3. Thus, these results demonstrated that natural extracts could have applications as natural preservatives in meat products.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Antioxidant Determinations by the Use of a Stable Free Radical

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Comprehensive Review on Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found