- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A systematic review of technologies and standards used in the development of rule-based clinical decision support systems
Read this article at
Abstract
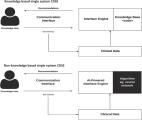
A Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) is a technology platform that uses medical knowledge with clinical data to provide customised advice for an individual patient's care. CDSSs use rules to encapsulate expert knowledge and rules engines to infer logic by evaluating rules according to a patient's specific information and related medical facts. However, CDSSs are by nature complex with a plethora of different technologies, standards and methods used to implement them and it can be difficult for practitioners to determine an appropriate solution for a specific scenario. This study's main goal is to provide a better understanding of different technical aspects of a CDSS, identify gaps in CDSS development and ultimately provide some guidelines to assist their translation into practice. We focus on issues related to knowledge representation including use of clinical ontologies, interoperability with EHRs, technology standards, CDSS architecture and mobile/cloud access.
This study performs a systematic literature review of rule-based CDSSs that discuss the underlying technologies used and have evaluated clinical outcomes. From a search that yielded an initial set of 1731 papers, only 15 included an evaluation of clinical outcomes. This study has found that a large majority of papers did not include any form of evaluation and, for many that did include an evaluation, the methodology was not sufficiently rigorous to provide statistically significant results. From the 15 papers shortlisted, there were no RCT or quasi-experimental studies, only 6 used ontologies to represent domain knowledge, only 2 integrated with an EHR system, only 5 supported mobile use and only 3 used recognised healthcare technology standards (and all these were HL7 standards). Based on these findings, the paper provides some recommendations for future CDSS development.
Related collections
Most cited references47

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
An overview of clinical decision support systems: benefits, risks, and strategies for success
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found