- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
An overview of clinical decision support systems: benefits, risks, and strategies for success
Read this article at
Abstract
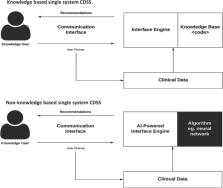
Computerized clinical decision support systems, or CDSS, represent a paradigm shift in healthcare today. CDSS are used to augment clinicians in their complex decision-making processes. Since their first use in the 1980s, CDSS have seen a rapid evolution. They are now commonly administered through electronic medical records and other computerized clinical workflows, which has been facilitated by increasing global adoption of electronic medical records with advanced capabilities. Despite these advances, there remain unknowns regarding the effect CDSS have on the providers who use them, patient outcomes, and costs. There have been numerous published examples in the past decade(s) of CDSS success stories, but notable setbacks have also shown us that CDSS are not without risks. In this paper, we provide a state-of-the-art overview on the use of clinical decision support systems in medicine, including the different types, current use cases with proven efficacy, common pitfalls, and potential harms. We conclude with evidence-based recommendations for minimizing risk in CDSS design, implementation, evaluation, and maintenance.
Related collections
Most cited references102
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found