- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
MERS coronavirus: diagnostics, epidemiology and transmission
Read this article at
Abstract
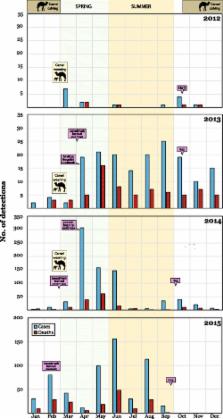
The first known cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), associated with infection by a novel coronavirus (CoV), occurred in 2012 in Jordan but were reported retrospectively. The case first to be publicly reported was from Jeddah, in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). Since then, MERS-CoV sequences have been found in a bat and in many dromedary camels (DC). MERS-CoV is enzootic in DC across the Arabian Peninsula and in parts of Africa, causing mild upper respiratory tract illness in its camel reservoir and sporadic, but relatively rare human infections. Precisely how virus transmits to humans remains unknown but close and lengthy exposure appears to be a requirement. The KSA is the focal point of MERS, with the majority of human cases. In humans, MERS is mostly known as a lower respiratory tract (LRT) disease involving fever, cough, breathing difficulties and pneumonia that may progress to acute respiratory distress syndrome, multiorgan failure and death in 20 % to 40 % of those infected. However, MERS-CoV has also been detected in mild and influenza-like illnesses and in those with no signs or symptoms. Older males most obviously suffer severe disease and MERS patients often have comorbidities. Compared to severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), another sometimes- fatal zoonotic coronavirus disease that has since disappeared, MERS progresses more rapidly to respiratory failure and acute kidney injury (it also has an affinity for growth in kidney cells under laboratory conditions), is more frequently reported in patients with underlying disease and is more often fatal. Most human cases of MERS have been linked to lapses in infection prevention and control (IPC) in healthcare settings, with approximately 20 % of all virus detections reported among healthcare workers (HCWs) and higher exposures in those with occupations that bring them into close contact with camels. Sero-surveys have found widespread evidence of past infection in adult camels and limited past exposure among humans. Sensitive, validated reverse transcriptase real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-rtPCR)-based diagnostics have been available almost from the start of the emergence of MERS. While the basic virology of MERS-CoV has advanced over the past three years, understanding of the interplay between camel, environment, and human remains limited.
Related collections
Most cited references213
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found