- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Highly cross-linked polyethylene still outperforms conventional polyethylene in THA: 10-year RSA results
Read this article at
Abstract
Background and purpose — Cup wear in total hip arthroplasty (THA) can be affected by different manufacturing processes of the polyethylene (PE). We report the long-term wear pattern differences, as well as early creep behavior, between conventional PE and highly cross-linked PE (HXLPE) liners, as measured with radiostereometry (RSA) up to 10 years. We also compare migration and clinical outcome of 2 similar uncemented cups with different backside surface roughness.
Patients and methods — We included 45 patients with primary osteoarthritis. 23 received a conventional liner and 22 an HXLPE liner in a similar uncemented cup, but with a slightly rougher surface. The patients were followed up with RSA and hip-specific outcome questionnaire (HOOS) at 3 months, 1, 2, 5, and 10 years.
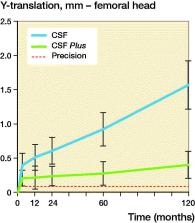
Results — During the first 3 months both liners showed expected deformation with mean proximal head penetration of 0.39 mm (conventional PE) and 0.21 mm (HXLPE). Between 3 months and 10 years there was a difference in annual wear with 0.12 mm/year for the conventional liner and 0.02 mm/year for the HXLPE liner. The cup with rougher surface had less initial migration but both types had stabilized after 3 months. The HOOS scores improved after surgery and remained high for both groups throughout the study period.
Interpretation — Up to 10 years the HXLPE has consistent lower annual wear, possibly contributing to longer survival of the THA, compared with conventional PE. All patients reported good results regardless of liner type.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Guidelines for standardization of radiostereometry (RSA) of implants.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Hip disability and osteoarthritis outcome score (HOOS) – validity and responsiveness in total hip replacement
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found