- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Integration of exercise prescription into medical provision as a treatment for non-communicable diseases: A scoping review
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The purpose of this scoping review is to stimulate interest and to raise awareness, among researchers, healthcare practitioners, and policymakers regarding the current scientific literature related to exercise prescription for non-communicable diseases (NCDs). Exercise prescription is a safe and cost-effective method that enables physicians to use exercise as a complementary addition to NCDs management and treatment.
Methods
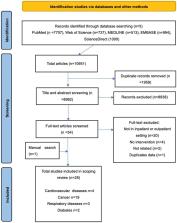
This scoping review followed the PRISMA Extension Guidelines for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Using this framework, we considered information from qualitative and quantitative studies to identify research gaps. We provide feasible suggestions to guide future research for the implementation of exercise prescription in the healthcare environment. The literature search was conducted using SPIDER and PICO tools for qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-study designs. Inclusion criteria included articles that investigated patients with NCDs and considered exercise interventions. Systematic searches of PubMed, Web of Science, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and ScienceDirect were undertaken on 26 July 2022 and all reference lists were manually searched. Data processing was performed using EndNote 2.0 software and data charts were used for numerical summary and thematic analysis.
Results
There were 10,951 articles retrieved, of which 28 met the inclusion criteria. Based on the evidence, exercise was a feasible, safe, and acceptable method to prevent and manage non-communicable diseases in inpatient and outpatient settings. Six research directions were identified and discussed. In addition, implementation evidence and suggestions for policy-reconfiguration are also provided.
Conclusion
This scoping review summarizes the current evidence for the effectiveness of exercise in the treatment of non-communicable diseases. The review provides key findings supporting exercise prescription for the inpatient and outpatient healthcare service. We suggest that governments and healthcare policymakers globally advocate the inclusion of structured exercise prescription within the NCDs treatment setting.
Related collections
Most cited references62
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found