- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Co-occurrence of resistance genes to antibiotics, biocides and metals reveals novel insights into their co-selection potential
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Antibacterial biocides and metals can co-select for antibiotic resistance when bacteria harbour resistance or tolerance genes towards both types of compounds. Despite numerous case studies, systematic and quantitative data on co-occurrence of such genes on plasmids and chromosomes is lacking, as is knowledge on environments and bacterial taxa that tend to carry resistance genes to such compounds. This effectively prevents identification of risk scenarios. Therefore, we aimed to identify general patterns for which biocide/metal resistance genes (BMRGs) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) that tend to occur together. We also aimed to quantify co-occurrence of resistance genes in different environments and taxa, and investigate to what extent plasmids carrying both types of genes are conjugative and/or are carrying toxin-antitoxin systems.
Results
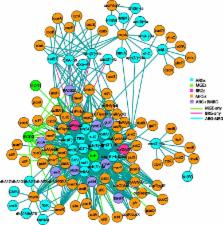
Co-occurrence patterns of resistance genes were derived from publicly available, fully sequenced bacterial genomes ( n = 2522) and plasmids ( n = 4582). The only BMRGs commonly co-occurring with ARGs on plasmids were mercury resistance genes and the qacE∆1 gene that provides low-level resistance to quaternary ammonium compounds. Novel connections between cadmium/zinc and macrolide/aminoglycoside resistance genes were also uncovered. Several clinically important bacterial taxa were particularly prone to carry both BMRGs and ARGs. Bacteria carrying BMRGs more often carried ARGs compared to bacteria without ( p < 0.0001). BMRGs were found in 86 % of bacterial genomes, and co-occurred with ARGs in 17 % of the cases. In contrast, co-occurrences of BMRGs and ARGs were rare on plasmids from all external environments (<0.7 %) but more common on those of human and domestic animal origin (5 % and 7 %, respectively). Finally, plasmids with both BMRGs and ARGs were more likely to be conjugative ( p < 0.0001) and carry toxin-antitoxin systems ( p < 0.0001) than plasmids without resistance genes.
Conclusions
This is the first large-scale identification of compounds, taxa and environments of particular concern for co-selection of resistance against antibiotics, biocides and metals. Genetic co-occurrences suggest that plasmids provide limited opportunities for biocides and metals to promote horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance through co-selection, whereas ample possibilities exist for indirect selection via chromosomal BMRGs. Taken together, the derived patterns improve our understanding of co-selection potential between biocides, metals and antibiotics, and thereby provide guidance for risk-reducing actions.
Related collections
Most cited references24
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Deletional bias and the evolution of bacterial genomes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found