- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Successional Distance between the Source and Recipient Influence Seed Germination and Seedling Survival during Surface Soil Replacement in SW China
Read this article at
Abstract
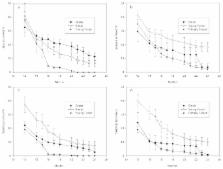
Adding propagules (source) to a degraded site (recipient) is a common way of manipulating secondary succession to restore diversity and services formerly provided by forests. However, heretofore no study has considered the effect of “successional distance” between source and recipient site. Four sites in the Shilin karst area of SW China were treated as different states along a secondary successional sere: grass, shrub, young secondary forest, and primary forest. Ten 1 m ×1m soil quadrats in the grass, shrub and young forest sites were replaced with 10 cm deep soil sources from corresponding later successional stage(s) in January 2009. Woody plant seed germination was monitored in the first year and seedling survival was monitored until the end of the second year. At the end of 2010, 2097 seeds of woody plants belonging to 45 taxa had germinated, and 3.9% of the seedlings and 7.8% of the species survived. Germination of most species was sensitive to ambient light (red, far-red, R:FR ratios, photosynthetically active radiation). Soil source and recipient site had a significant effect on the total number of seeds and number of species that germinated, and on the percentage of seedlings that survived through the end of the second year. Closer successional stages between recipient site and soil source had higher seed germination and seedling-survival percentages. However, a transition threshold exists in the young forest state, where seeds can germinate but not survive the second year. Our results, although based on an unreplicated chronosequence, suggest that successional distance between soil sources and recipient sites affect forest recruitment and restoration in degraded karst of SW China.
Related collections
Most cited references3
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Ecology. Hurdles and opportunities for landscape-scale restoration.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Are plant populations seed limited? A critique and meta-analysis of seed addition experiments.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found