- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Identification of Hypericin as a Candidate Repurposed Therapeutic Agent for COVID-19 and Its Potential Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity
Read this article at
Abstract
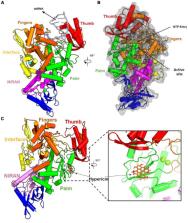
The COVID-19 pandemic has had an unprecedented impact on the global economy and public health. Its etiologic agent, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is highly transmissible, pathogenic and has a rapid global spread. Currently, the increase in the number of new confirmed cases has been slowed down due to the increase of vaccination in some regions of the world. Still, the rise of new variants has influenced the detection of additional waves of rising cases that some countries have experienced. Since the virus replication cycle is composed of many distinct stages, some viral proteins related to them, as the main-protease (Mpro) and RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), constitute individual potential antiviral targets. In this study, we challenged the mentioned enzymes against compounds pre-approved by health regulatory agencies in a virtual screening and later in Molecular Mechanics/Poisson–Bolzmann Surface Area (MM/PBSA) analysis. Our results showed that, among the identified potential drugs with anti-SARS-CoV-2 properties, Hypericin, an important component of the Hypericum perforatum that presents antiviral and antitumoral properties, binds with high affinity to viral Mpro and RdRp. Furthermore, we evaluated the activity of Hypericin anti-SARS-CoV-2 replication in an in vitro model of Vero-E6 infected cells. Therefore, we show that Hypericin inhibited viral replication in a dose dependent manner. Moreover, the cytotoxicity of the compound, in cultured cells, was evaluated, but no significant activity was found. Thus, the results observed in this study indicate that Hypericin is an excellent candidate for repurposing for the treatment of COVID-19, with possible inhibition of two important phases of virus maturation.
Related collections
Most cited references70
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Protein Data Bank.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found