- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The role of natural products from medicinal plants against COVID-19: traditional medicine practice in Tanzania
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Pandemic COVID-19 is a dangerous disease caused by a new coronavirus known as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2). There is non-reliable drug or vaccine available to combat for SARS-CoV-2. More efforts to search for antiviral agents against COVID-19 are obligatory, whereas phytochemicals are potent solution. Thus, this study involved phytochemical screening and examining medicinal plants used to combat COVID-19 in Tanzania.
Methods
The plant materials were collected from practitioners. The plant extracts were then subjected for qualitative phytochemical screening so as to identify the nature of secondary metabolites.
Results
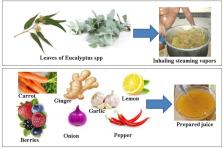
Eucalyptus species, pepper, berries, ginger, garlic, onions and lemon were identified as commonly plants used. The flavonoids, tannins, fatty acids, steroids, terpenoids, and saponins were identified through phytochemical screening. Identified natural phytocompounds revealed to be potential in exhibiting antiviral activities by disrupting the viral life cycle including viral entrance, replication, assembly, and discharge, as well as virus-specific host targets. Thus, this prompt increasing of pharmaceutical industry focused on phytochemical extracts from medicinal plants, and aromatic herbs in the hopes of discovering lead compounds, with purposeful to antiviral medications.
Conclusion
The medicinal plants and phytocompounds revealed to have significant role due to their substantial antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses. The noted natural products inspire collective efforts in determination and gathering funds to support scientific researchers to investigate more phytochemicals from medicinal plants for development of antiviral drug against COVID-19.
Graphical abstract
Abstract
COVID-19; Phytochemicals; Medicinal plants; Antiviral drugs; Phytochemical screening.
Related collections
Most cited references41
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Genome Composition and Divergence of the Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Originating in China

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Bioactive flavonoids in medicinal plants: Structure, activity and biological fate

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
