- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Systematic scoping review of the implementation, adoption, use, and effectiveness of digital contact tracing interventions for COVID-19 in the Western Pacific Region

Read this article at
Abstract
A systematic scoping review of digital contact tracing (DCT) interventions for COVID-19 was conducted to describe the implementation, adoption, use and effectiveness of DCT interventions implemented as part of the COVID-19 response in the Western Pacific Region (WPR). A systematic search identified 341 studies and 128 grey literature sources, of which 18 studies and 41 grey literature sources were included. 17 (46%) WPR countries and areas implemented DCT interventions. Adoption ranged from 14.6% to 92.7% in different adult populations and epidemiological contexts. Trust in authorities, and privacy concerns and beliefs, were the most frequent determinants of adoption and use. Only two studies analysed DCT effectiveness, which showed limited to no effectiveness of DCT interventions in low transmission settings. Overall, there is limited evidence available to evaluate the contribution of DCT to mitigating COVID-19 in the WPR. Preparedness for future health emergencies should include developing robust frameworks for DCT effectiveness evaluations.
Related collections
Most cited references48
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
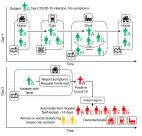
Quantifying SARS-CoV-2 transmission suggests epidemic control with digital contact tracing

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
