- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Climate Change and Food Systems
Read this article at
Abstract
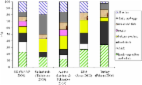
Food systems contribute 19%–29% of global anthropogenic greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, releasing 9,800–16,900 megatonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (MtCO2e) in 2008. Agricultural production, including indirect emissions associated with land-cover change, contributes 80%–86% of total food system emissions, with significant regional variation. The impacts of global climate change on food systems are expected to be widespread, complex, geographically and temporally variable, and profoundly influenced by socioeconomic conditions. Historical statistical studies and integrated assessment models provide evidence that climate change will affect agricultural yields and earnings, food prices, reliability of delivery, food quality, and, notably, food safety. Low-income producers and consumers of food will be more vulnerable to climate change owing to their comparatively limited ability to invest in adaptive institutions and technologies under increasing climatic risks. Some synergies among food security, adaptation, and mitigation are feasible. But promising interventions, such as agricultural intensification or reductions in waste, will require careful management to distribute costs and benefits effectively.
Related collections
Most cited references90
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Food waste within food supply chains: quantification and potential for change to 2050
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found