- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Identifying the potential causal role of insomnia symptoms on 11,409 health-related outcomes: a phenome-wide Mendelian randomisation analysis in UK Biobank
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Insomnia symptoms are widespread in the population and might have effects on many chronic conditions and their risk factors but previous research has focused on select hypothesised associations/effects rather than taking a systematic hypothesis-free approach across many health outcomes.
Methods
We performed a Mendelian randomisation (MR) phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) in 336,975 unrelated white-British UK Biobank participants. Self-reported insomnia symptoms were instrumented by a genetic risk score (GRS) created from 129 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). A total of 11,409 outcomes from UK Biobank were extracted and processed by an automated pipeline (PHESANT) for the MR-PheWAS. Potential causal effects (those passing a Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold) were followed up with two-sample MR in MR-Base, where possible.
Results
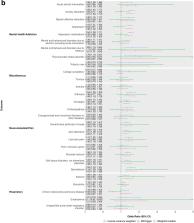
Four hundred thirty-seven potential causal effects of insomnia symptoms were observed for a diverse range of outcomes, including anxiety, depression, pain, body composition, respiratory, musculoskeletal and cardiovascular traits. We were able to undertake two-sample MR for 71 of these 437 and found evidence of causal effects (with directionally concordant effect estimates across main and sensitivity analyses) for 30 of these. These included novel findings (by which we mean not extensively explored in conventional observational studies and not previously explored using MR based on a systematic search) of an adverse effect on risk of spondylosis (OR [95%CI] = 1.55 [1.33, 1.81]) and bronchitis (OR [95%CI] = 1.12 [1.03, 1.22]), among others.
Related collections
Most cited references49
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A global reference for human genetic variation

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found