- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Phase 1/2 study of pacritinib, a next generation JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor, in myelofibrosis or other myeloid malignancies
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Pacritinib (SB1518) is a highly selective kinase inhibitor with specificity for JAK2, FLT3, IRAK1, and CFS1R. This multicenter phase 1/2 study evaluated the maximum tolerated dose (MTD), safety, and clinical activity of pacritinib in patients with myelofibrosis (MF) and other advanced myeloid malignancies.
Methods
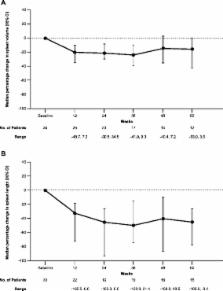
In the phase 1 dose-escalation part of the study, 43 adults with advanced myeloid malignancies received pacritinib 100 to 600 mg once daily (QD). In the phase 2 part of the study, 31 adults with refractory or intermediate- or high-risk newly diagnosed MF and any degree of cytopenia received pacritinib 400 mg QD. The primary endpoint is a ≥35% reduction in spleen volume at week 24 as determined by magnetic resonance imaging.
Results
Five patients (11.6%) experienced a dose-limiting toxicity during cycle 1 of phase 1. The clinical benefit rate was 86.0% (13 patients achieving clinical improvement and 24 patients having stable disease). The MTD was established at 500 mg QD, and the recommended phase 2 dose was 400 mg QD. In phase 2, the primary endpoint was achieved by 23.5% of evaluable patients (4/17), with 47.4% (9/19) achieving a ≥50% spleen length reduction at week 24 as measured by physical examination. At week 24, 38.9% of evaluable patients (7/18) achieved a ≥50% decrease in MF Quality of Life and Symptom Assessment total score. Gastrointestinal toxicities were the most common adverse events and were predominantly grade 1/2 in severity. Grade 3/4 anemia was reported in 5/31 patients and grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia was reported in 3/31 patients. The most frequent AEs considered to be treatment related were diarrhea (28/31), nausea (15/31), vomiting (9/31), and fatigue (4/31). Grade 3 treatment-related AEs were reported in seven patients (22.6%), four of whom had diarrhea. No grade 4/5 treatment-related AEs were reported. No leukopenia, neutropenia, or lymphopenia were reported.
Conclusions
Pacritinib was well tolerated and demonstrated clinical activity in MF. The study suggests that pacritinib has unique characteristics, namely a lack of substantial myelosuppression and manageable side effects, making it an attractive target for further evaluation in MF.
Trial registration
Retrospectively registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov (# NCT00719836) on July 20, 2008.
Related collections
Most cited references18
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical application and proposal for modification of the International Working Group (IWG) response criteria in myelodysplasia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Analysis of FLT3-activating mutations in 979 patients with acute myelogenous leukemia: association with FAB subtypes and identification of subgroups with poor prognosis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found