- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Screening for posttraumatic stress disorder in ARDS survivors: validation of the Impact of Event Scale-6 (IES-6)
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms are common in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) survivors. Brief screening instruments are needed for clinical and research purposes. We evaluated internal consistency, external construct, and criterion validity of the Impact of Event Scale-6 (IES-6; 6 items) compared to the original Impact of Event Scale—Revised (IES-R; 22 items) and to the Clinician Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) reference standard evaluation in ARDS survivors.
Methods
This study is a secondary analysis from two independent multi-site, prospective studies of ARDS survivors. Measures of internal consistency, and external construct and criterion validity were evaluated.
Results
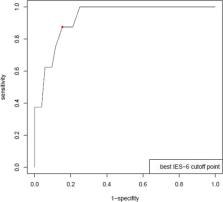
A total of 1001 ARDS survivors (51% female, 76% white, mean (SD) age 49 (14) years) were evaluated. The IES-6 demonstrated internal consistency over multiple time points up to 5 years after ARDS (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.96; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.94 to 0.97). The IES-6 demonstrated stronger correlations with related constructs (e.g., anxiety and depression; |r| = 0.32 to 0.52) and weaker correlations with unrelated constructs (e.g., physical function and healthcare utilization measures (|r| = 0.02 to 0.27). Criterion validity evaluation with the CAPS diagnosis of PTSD in a subsample of 60 participants yielded an area under receiver operating characteristic curve (95% CI) of 0.93 (0.86, 1.00), with an IES-6 cutoff score of 1.75 yielding 0.88 sensitivity and 0.85 specificity.
Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
EuroQol - a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found