- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Weighted single-step GWAS identified candidate genes associated with carcass traits in a Chinese yellow-feathered chicken population
Read this article at
Abstract
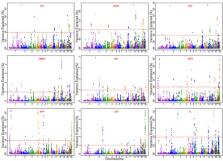
Carcass traits in broiler chickens are complex traits that are influenced by multiple genes. To gain deeper insights into the genetic mechanisms underlying carcass traits, here we conducted a weighted single-step genome-wide association study ( wssGWAS) in a population of Chinese yellow-feathered chicken. The objective was to identify genomic regions and candidate genes associated with carcass weight ( CW), eviscerated weight with giblets ( EWG), eviscerated weight ( EW), breast muscle weight ( BMW), drumstick weight ( DW), abdominal fat weight ( AFW), abdominal fat percentage ( AFP), gizzard weight ( GW), and intestine length ( IL). A total of 1,338 broiler chickens with phenotypic and pedigree information were included in this study. Of these, 435 chickens were genotyped using a 600K single nucleotide polymorphism chip for association analysis. The results indicate that the most significant regions for 9 traits explained 2.38% to 5.09% of the phenotypic variation, from which the region of 194.53 to 194.63Mb on chromosome 1 with the gene RELT and FAM168A identified on it was significantly associated with CW, EWG, EW, BMW, and DW. Meanwhile, the 5 traits have a strong genetic correlation, indicating that the region and the genes can be used for further research. In addition, some candidate genes associated with skeletal muscle development, fat deposition regulation, intestinal repair, and protection were identified. Gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analyses suggested that the genes are involved in processes such as vascular development ( CD34, FGF7, FGFR3, ITGB1BP1, SEMA5A, LOXL2), bone formation ( FGFR3, MATN1, MEF2D, DHRS3, SKI, STC1, HOXB1, HOXB3, TIPARP), and anatomical size regulation ( ADD2, AKT1, CFTR, EDN3, FLII, HCLS1, ITGB1BP1, SEMA5A, SHC1, ULK1, DSTN, GSK3B, BORCS8, GRIP2 ). In conclusion, the integration of phenotype, genotype, and pedigree information without creating pseudo-phenotype will facilitate the genetic improvement of carcass traits in chickens, providing valuable insights into the genetic architecture and potential candidate genes underlying carcass traits, enriching our understanding and contributing to the breeding of high-quality broiler chickens.
Related collections
Most cited references95

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found