- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Awareness of fetal movements and care package to reduce fetal mortality (AFFIRM): a stepped wedge, cluster-randomised trial
Read this article at
Summary
Background
2·6 million pregnancies were estimated to have ended in stillbirth in 2015. The aim of the AFFIRM study was to test the hypothesis that introduction of a reduced fetal movement (RFM), care package for pregnant women and clinicians that increased women's awareness of the need for prompt reporting of RFM and that standardised management, including timely delivery, would alter the incidence of stillbirth.
Methods
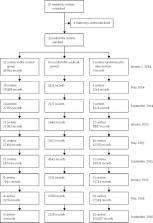
This stepped wedge, cluster-randomised trial was done in the UK and Ireland. Participating maternity hospitals were grouped and randomised, using a computer-generated allocation scheme, to one of nine intervention implementation dates (at 3 month intervals). This date was concealed from clusters and the trial team until 3 months before the implementation date. Each participating hospital had three observation periods: a control period from Jan 1, 2014, until randomised date of intervention initiation; a washout period from the implementation date and for 2 months; and the intervention period from the end of the washout period until Dec 31, 2016. Treatment allocation was not concealed from participating women and caregivers. Data were derived from observational maternity data. The primary outcome was incidence of stillbirth. The primary analysis was done according to the intention-to-treat principle, with births analysed according to whether they took place during the control or intervention periods, irrespective of whether the intervention had been implemented as planned. This study is registered with www.ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT01777022.
Findings
37 hospitals were enrolled in the study. Four hospitals declined participation, and 33 hospitals were randomly assigned to an intervention implementation date. Between Jan 1, 2014, and Dec, 31, 2016, data were collected from 409 175 pregnancies (157 692 deliveries during the control period, 23 623 deliveries in the washout period, and 227 860 deliveries in the intervention period). The incidence of stillbirth was 4·40 per 1000 births during the control period and 4·06 per 1000 births in the intervention period (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0·90, 95% CI 0·75–1·07; p=0·23).
Related collections
Most cited references24

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The REporting of studies Conducted using Observational Routinely-collected health Data (RECORD) Statement
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
International standards for newborn weight, length, and head circumference by gestational age and sex: the Newborn Cross-Sectional Study of the INTERGROWTH-21st Project.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found