- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Loneliness during a strict lockdown: Trajectories and predictors during the COVID-19 pandemic in 38,217 United Kingdom adults
Abstract
Rationale
There are increasing worries that lockdowns and ‘stay-at-home’ orders due to the COVID-19 pandemic could lead to a rise in loneliness, which is recognised as a major public health concern. But profiles of loneliness during the pandemic and risk factors remain unclear.
Objective
The current study aimed to examine if and how loneliness levels changed during the strict lockdown and to explore the clustering of loneliness growth trajectories.
Methods
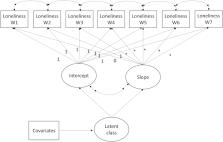
Data from 38,217 UK adults in the UCL COVID -19 Social Study (a panel study collecting data weekly during the pandemic) were analysed during the strict lockdown period in the UK (23/03/2020–10/05/2020). The sample was well-stratified and weighted to population proportions of gender, age, ethnicity, education and geographical location. Growth mixture modelling was used to identify the latent classes of loneliness growth trajectories and their predictors.
Results
Analyses revealed four classes, with the baseline loneliness level ranging from low to high. In the first a few weeks of lockdown, loneliness levels increased in the highest loneliness group, decreased in the lowest loneliness group, and stayed relatively constant in the middle two groups. Younger adults (OR = 2.17–6.81), women (OR = 1.59), people with low income (OR = 1.3), the economically inactive (OR = 1.3–2.04) and people with mental health conditions (OR = 5.32) were more likely to be in highest loneliness class relative to the lowest. Further, living with others or in a rural area, and having more close friends or greater social support were protective.
Highlights
-
•
Our analyses revealed four distinctive latent classes of loneliness trajectories.
-
•
During the seven weeks of strict lockdown, loneliness levels were relatively stable.
-
•
There is a slight increase in the highest loneliness class and decrease in the lowest class.
-
•
A range of demographic, health, and social factors were related to latent classes.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: a call for action for mental health science
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Mental Health Consequences of COVID-19 and Physical Distancing: The Need for Prevention and Early Intervention
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found