- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A developed high-performance thin-layer chromatography method for the determination of baicalin in Oroxylum indicum L. and its antioxidant activity
Read this article at
Abstract
Abstract
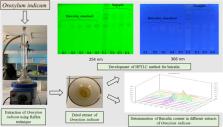
A simple, accurate, precise, and specific high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) method for the quantitative determination and validation of baicalin in different extracts of Oroxylum indicum has been developed for the first time. The mobile phase of acetone‒ethyl acetate‒water‒formic acid (2:10:0.5:0.5, V/V) was used for achieving good separation. Densitometric determination was carried out at 318 nm. The calibration curves were found to be linear in the range between 200 and 1000 ng per spot. During the analysis, the ethanolic extract of O. indicum showed higher content of baicalin than acetone, DMSO, and DMF extracts. Further, the antioxidant potential of different extracts of O. indicum were assessed with the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) method. The developed method of HPTLC was validated for specificity, accuracy, precision and linearity. The ethanolic extract has unveiled significant antioxidant activity with a percentage inhibition of 67.34%.
Related collections
Most cited references33
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Therapeutic potentials of baicalin and its aglycone, baicalein against inflammatory disorders.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz, an important Asian traditional medicine: from traditional uses to scientific data for its commercial exploitation.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found

