- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Endogenous florendoviruses are major components of plant genomes and hallmarks of virus evolution
Read this article at
Abstract
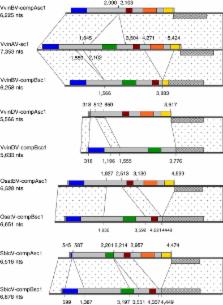
The extent and importance of endogenous viral elements have been extensively described in animals but are much less well understood in plants. Here we describe a new genus of Caulimoviridae called ‘Florendovirus’, members of which have colonized the genomes of a large diversity of flowering plants, sometimes at very high copy numbers (>0.5% total genome content). The genome invasion of Oryza is dated to over 1.8 million years ago (MYA) but phylogeographic evidence points to an even older age of 20–34 MYA for this virus group. Some appear to have had a bipartite genome organization, a unique characteristic among viral retroelements. In Vitis vinifera, 9% of the endogenous florendovirus loci are located within introns and therefore may influence host gene expression. The frequent colocation of endogenous florendovirus loci with TA simple sequence repeats, which are associated with chromosome fragility, suggests sequence capture during repair of double-stranded DNA breaks.
Abstract
 Endogenous viral elements have been extensively described in animals but their significance
in plants is less well understood. Here, Geering
et al. describe a new group of endogenous pararetroviruses, called florendoviruses, which
have colonized the genomes of many important crop species.
Endogenous viral elements have been extensively described in animals but their significance
in plants is less well understood. Here, Geering
et al. describe a new group of endogenous pararetroviruses, called florendoviruses, which
have colonized the genomes of many important crop species.
Related collections
Most cited references45
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Horizontal gene transfer in eukaryotic evolution.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
AWTY (are we there yet?): a system for graphical exploration of MCMC convergence in Bayesian phylogenetics.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found