- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Antiviral/antibacterial biodegradable cellulose nonwovens as environmentally friendly and bioprotective materials with potential to minimize microplastic pollution
Abstract
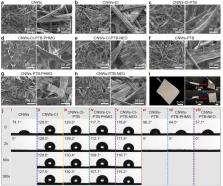
Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as face masks is vital in battling the COVID-19 crisis, but the dominant polypropylene-based PPE are lack of antiviral/antibacterial activities and environmental friendliness, and have hazardous impact on the soil and aquatic ecosystems. The work presented herein focused on developing biodegradable, antiviral, and antibacterial cellulose nonwovens (AVAB-CNWs) as a multi-functional bioprotective layer for better protection against coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and addressing environmental concerns raised by the piling of COVID-19 related wastes. Both guanidine-based polymer and neomycin sulfate (NEO) were reactive-modified and covalently grafted onto the surface of cellulose nonwovens, thereby conferring outstanding antiviral and antibacterial activities to the nonwovens without deteriorating the microstructure and biodegradability. Through adjusting the grafting amount of active components and selecting appropriate reagents for pretreatment, the antimicrobial activity and hydrophobicity for self-cleaning of the nonwovens can be tuned. More importantly, we demonstrated for the first time that such multi-functional nonwovens are capable of inactivating SARS-CoV-2 instantly, leading to high virucidal activity (>99.35%), which is unachievable by conventional masks used nowadays. Meanwhile, the robust breathability and biodegradability of AVAB-CNWs were well maintained. The applications of the as-prepared nonwovens as high-performance textile can be readily extended to other areas in the fight against COVID-19.
Graphical abstract
Related collections
Most cited references61
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Critical Supply Shortages — The Need for Ventilators and Personal Protective Equipment during the Covid-19 Pandemic
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found

