- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effects of Environmental Factors on Concrete Carbonation Depth and Compressive Strength
Read this article at
Abstract
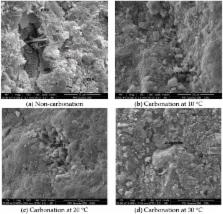
The influence of temperature, CO 2 concentration and relative humidity on the carbonation depth and compressive strength of concrete was investigated. Meanwhile, phase composition, types of hydration products and microstructure characteristics of samples before and after the carbonation were analyzed by XRD and ESEM. Research results demonstrate that temperature, CO 2 concentration and relative humidity influence the carbonation depth and compressive strength of concrete significantly. There is a linear relationship between temperature and carbonation depth, as well as the compressive strength of concrete. CO 2 concentration and relative humidity present a power function and a polynomial function with carbonation depth of concrete, respectively. The concrete carbonation depth increases with the increase of relative humidity and reaches the maximum value when the relative humidity is 70%. Significant differences of phase composition, hydration products and microstructure are observed before and after the carbonation. Carbonization products of samples are different with changes of temperatures (10 °C, 20 °C and 30 °C). The result of crystal structure analysis indicates that the carbonation products are mainly polyhedral spherical vaterite and aragonite.
Related collections
Most cited references24
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The experimental investigation of concrete carbonation depth
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Accelerated carbonation and testing of concrete made with fly ash
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found