- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Transition from Diffusive to Superdiffusive Transport in Carbon Nanotube Networks via Nematic Order Control

Read this article at
Abstract
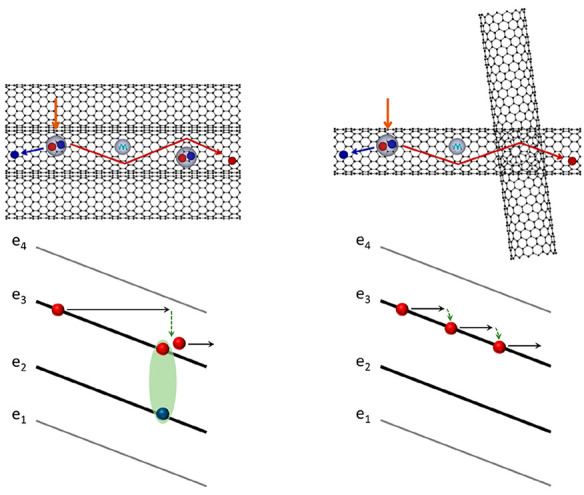
The one-dimensional confinement of quasiparticles in individual carbon nanotubes (CNTs) leads to extremely anisotropic electronic and optical properties. In a macroscopic ensemble of randomly oriented CNTs, this anisotropy disappears together with other properties that make them attractive for certain device applications. The question however remains if not only anisotropy but also other types of behaviors are suppressed by disorder. Here, we compare the dynamics of quasiparticles under strong electric fields in aligned and random CNT networks using a combination of terahertz emission and photocurrent experiments and out-of-equilibrium numerical simulations. We find that the degree of alignment strongly influences the excited quasiparticles’ dynamics, rerouting the thermalization pathways. This is, in particular, evidenced in the high-energy, high-momentum electronic population (probed through the formation of low energy excitons via exciton impact ionization) and the transport regime evolving from diffusive to superdiffusive.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found