- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cancer Drugs Reimbursed with Limited Evidence on Overall Survival and Quality of Life: Do Follow-Up Studies Confirm Patient Benefits?
Read this article at
Abstract
Background and Objective
Cancer drug costs have increased considerably within healthcare systems, but many drugs lack quality-of-life (QoL) and overall survival (OS) data at the time of reimbursement approval. This study aimed to review the extent of subsequent literature documenting improvements in OS and QoL for cancer drug indications where no such evidence existed at the time of reimbursement approval.
Methods
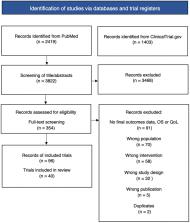
Drug indications with claims of added therapeutical value but a lack of evidence on OS and QoL that were reimbursed between 2010 and 2020 in Sweden were included for review. Searches were conducted in PubMed and ClinicalTrial.gov for randomized controlled trials examining OS and QoL.
Results
Of the 22 included drug indications, seven were found to have at least one trial with conclusive evidence of improvements in OS or QoL after a mean follow-up of 6.6 years. The remaining 15 drug indications either lacked subsequent randomized controlled trial data on OS or QoL ( n = 6) or showed no statistically significant improvements ( n = 9). Only one drug demonstrated evidence of improvement in both OS and QoL for its indication.
Conclusions
A considerable share of reimbursed cancer drug indications continue to lack evidence of improvement in both OS and QoL. With limited healthcare resources and an increasing cancer burden, third-party payers have strong incentives to require additional post-reimbursement data to confirm any improvements in OS and QoL.
Related collections
Most cited references70
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
