- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Management
Read this article at
Abstract
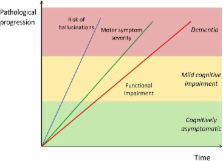
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common, disabling, neurodegenerative disorder. In addition to classical motor symptoms, non-motor features are now widely accepted as part of the clinical picture, and cognitive decline is a very important aspect of the disease, as it brings an additional significant burden for the patient and caregivers. The diagnosis of cognitive decline in PD, namely mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and dementia, can be extremely challenging, remaining largely based on clinical and cognitive assessments. Diagnostic criteria and methods for PD dementia and MCI have been recently issued by expert work groups. This manuscript has synthesized relevant data in order to obtain a pragmatic and updated review regarding cognitive decline in PD, from milder stages to dementia. This text will summarize clinical features, diagnostic methodology, and therapeutic issues of clinical decline in PD. Relevant clinical genetic issues, including recent advances, will also be approached.
Related collections
Most cited references145
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The MoCA: well-suited screen for cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The distinct cognitive syndromes of Parkinson's disease: 5 year follow-up of the CamPaIGN cohort.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found