- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Serotonergic modulation of glutamate neurotransmission as a strategy for treating depression and cognitive dysfunction
Read this article at
Abstract
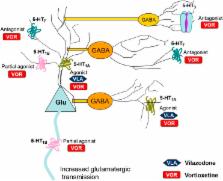
Monoamine-based treatments for depression have evolved greatly over the past several years, but shortcomings such as suboptimal efficacy, treatment lag, and residual cognitive dysfunction are still significant. Preclinical and clinical studies using compounds directly targeting glutamatergic neurotransmission present new opportunities for antidepressant treatment, with ketamine having a surprisingly rapid and sustained antidepressant effect that is presumably mediated through glutamate-dependent mechanisms. While direct modulation of glutamate transmission for antidepressant and cognition-enhancing actions may be hampered by nonspecific effects, indirect modulation through the serotonin (5-HT) system may be a viable alternative approach. Based on localization and function, 5-HT can modulate glutamate neurotransmission at least through the 5-HT 1A, 5-HT 1B, 5-HT 3, and 5-HT 7 receptors, which presents a rational pharmacological opportunity for modulating glutamatergic transmission without the direct use of glutamatergic compounds. Combining one or more of these glutamate-modulating 5-HT targets with 5-HT transporter inhibition may offer new therapeutic opportunities. The multimodal compounds vortioxetine and vilazodone are examples of this approach with diverse mechanisms, and their different clinical effects will provide valuable insights into serotonergic modulation of glutamate transmission for the potential treatment of depression and associated cognitive dysfunction.
Related collections
Most cited references133
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cellular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant effects of ketamine: role of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found