- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effect of Synthesis Method of La 1 − x Sr x MnO 3 Manganite Nanoparticles on Their Properties
Read this article at
Abstract
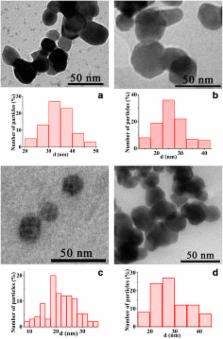
Nanoparticles of lanthanum-strontium manganite were synthesized via different methods, namely, sol-gel method, precipitation from non-aqueous solution, and precipitation from reversal microemulsions. It was shown that the use of organic compounds and non-aqueous media allowed significantly decreasing of the crystallization temperature of nanoparticles, and the single-phased crystalline product was formed in one stage. Morphology and properties of nanoparticles depended on the method and conditions of the synthesis. The heating efficiency directly depended on the change in the magnetic parameters of nanoparticles, especially on the magnetization. Performed studies showed that each of these methods of synthesis can be used to obtain weakly agglomerated manganite nanoparticles; however, particles synthesized via sol-gel method are more promising for use as hyperthermia inducers.
PACS: 61.46.Df 75.75.Cd 81.20. Fw
Related collections
Most cited references14
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Inductive heating of ferrimagnetic particles and magnetic fluids: Physical evaluation of their potential for hyperthermia
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Design of iron oxide-based nanoparticles for MRI and magnetic hyperthermia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found