- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Life cycle environmental impacts of disposable medical masks

Read this article at
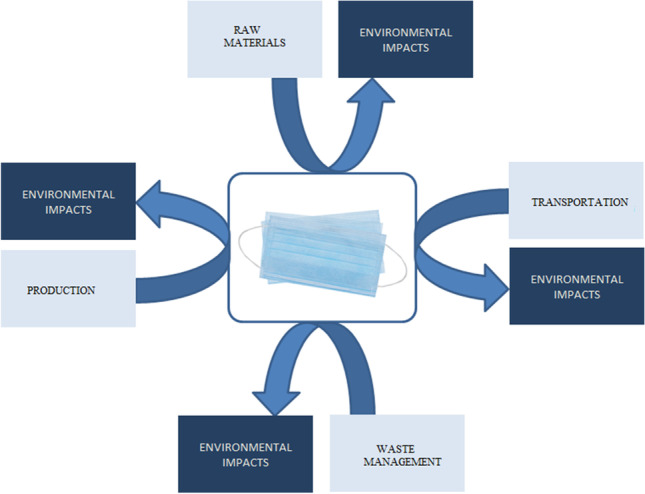
Graphical abstract
A massive increase in the use and production of masks worldwide has been seen in the current COVID-19 pandemic, which has contributed to reducing the transmission of the virus globally. This paper aims to evaluate the life cycle environmental impacts of disposable medical masks to identify the life cycle stages that cause the highest impact on the environment. A further goal is to estimate the total environmental impacts at the global level in 2020. The inventory data was constructed directly from the industry. The system boundary of the study is from cradle to grave comprising raw material extraction and processing, production, packaging, distribution, use, and disposal as well as transport and waste management along the supply chain. Eleven environmental impacts have been estimated. The results suggest that the global warming potential of a disposable medical mask is 0.02 g CO 2-eq. for which the main contributor is the raw material supply (40.5%) followed by the packaging (30.0%) and production (15.5%). Sensitivity analysis was carried out to test the environmental impacts. In total, 52 billion disposable medical masks used worldwide consumes 22 TJ of energy in 2020. The global warming potential of disposable medical masks supplied in a year of the COVID-19 pandemic is 1.1 Mt CO 2 eq. This paper assessed the hotspots in the medical mask. The findings of this study will be of interest to policymakers, global mask manufacturers, and users, allowing them to make more informed decisions about the medical mask industry.
Related collections
Most cited references12
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
SARS-CoV-2: an Emerging Coronavirus that Causes a Global Threat
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
