- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Conspiratorial Thinking During COVID-19: The Roles of Paranoia, Delusion-Proneness, and Intolerance of Uncertainty
Read this article at
Abstract
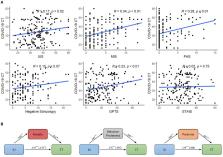
The COVID-19 global pandemic has left many feeling a sense of profound uncertainty about their world, safety, and livelihood. Sources espousing misinformation and conspiracy theories frequently offer information that can help make sense of this uncertainty. Individuals high in intolerance of uncertainty (IU) may be particularly impacted by the impoverished epistemic environment and may thus be more drawn to conspiratorial thinking (CT). In the present work, we show across 2 studies ( N = 519) that COVID-19-specific CT is associated with higher levels of IU as well as delusion-proneness, and paranoia. Furthermore, delusion-proneness and paranoia explained the relationship between IU and CT and emerged as independent partial correlates of CT even when controlling for other facets of schizotypy. In contrast, anxiety did not explain the relationship between IU and CT. Overall, our findings highlight the importance of individual differences in IU, delusion-proneness and paranoia in the development of CT in the context of the acute uncertainty of a global crisis, in which conspiracy theories are more prevalent and salient. Informational intervention designs may benefit from leveraging the body of work demonstrating the efficacy of targeting IU to incite meaningful changes in thinking.
Related collections
Most cited references65
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Using social and behavioural science to support COVID-19 pandemic response
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found