- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Genome and transcriptome analysis of the beet armyworm Spodoptera exigua reveals targets for pest control

Read this article at
Abstract
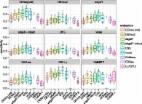
The genus Spodoptera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) includes some of the most infamous insect pests of cultivated plants including Spodoptera frugiperda, Spodoptera litura, and Spodoptera exigua. To effectively develop targeted pest control strategies for diverse Spodoptera species, genomic resources are highly desired. To this aim, we provide the genome assembly and developmental transcriptome comprising all major life stages of S. exigua, the beet armyworm. Spodoptera exigua is a polyphagous herbivore that can feed on > 130 host plants, including several economically important crops. The 419 Mb beet armyworm genome was sequenced from a female S. exigua pupa. Using a hybrid genome sequencing approach (Nanopore long-read data and Illumina short read), a high-quality genome assembly was achieved (N50 = 1.1 Mb). An official gene set (18,477 transcripts) was generated by automatic annotation and by using transcriptomic RNA-seq datasets of 18 S. exigua samples as supporting evidence. In-depth analyses of developmental stage-specific expression combined with gene tree analyses of identified homologous genes across Lepidoptera genomes revealed four potential genes of interest (three of them Spodoptera-specific) upregulated during first- and third-instar larval stages for targeted pest-outbreak management. The beet armyworm genome sequence and developmental transcriptome covering all major developmental stages provide critical insights into the biology of this devastating polyphagous insect pest species worldwide. In addition, comparative genomic analyses across Lepidoptera significantly advance our knowledge to further control other invasive Spodoptera species and reveals potential lineage-specific target genes for pest control strategies.
Related collections
Most cited references103
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found