- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effect of a low-cost, behaviour-change intervention on latrine use and safe disposal of child faeces in rural Odisha, India: a cluster-randomised controlled trial
Read this article at
Summary
Background
Uptake of Government-promoted sanitation remains a challenge in India. We aimed to investigate a low-cost, theory-driven, behavioural intervention designed to increase latrine use and safe disposal of child faeces in India.
Methods
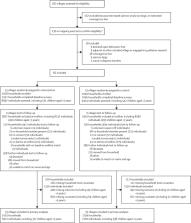
We did a cluster-randomised controlled trial between Jan 30, 2018, and Feb 18, 2019, in 66 rural villages in Puri, Odisha, India. Villages were eligible if not adjacent to another included village and not designated by the Government to be open-defecation free. All latrine-owning households in selected villages were eligible. We assigned 33 villages to the intervention via stratified randomisation. The intervention was required to meet a limit of US$20 per household and included a folk performance, transect walk, community meeting, recognition banners, community wall painting, mothers’ meetings, household visits, and latrine repairs. Control villages received no intervention. Neither participants nor field assessors were masked to study group assignment. We estimated intervention effects on reported latrine use and safe disposal of child faeces 4 months after completion of the intervention delivery using a difference-in-differences analysis and stratified results by sex. This study is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03274245.
Findings
We enrolled 3723 households (1807 [48·5%] in the intervention group and 1916 [51·5%] in the control group). Analysis included 14 181 individuals (6921 [48·8%] in the intervention group and 7260 [51·2%] in the control group). We found an increase of 6·4 percentage points (95% CI 2·0–10·7) in latrine use and an increase of 15·2 percentage points (7·9–22·5) in safe disposal of child faeces. No adverse events were reported.
Related collections
Most cited references30

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The behaviour change wheel: A new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Constructing socio-economic status indices: how to use principal components analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found