- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Intracranial hemorrhage in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Emerging evidence suggests that a subset of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients may present with or develop cerebrovascular disease during the course of hospitalization. Whereas ischemic stroke in COVID-19 patients has been well described, data on intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) in these patients is still limited. We, therefore, conducted a rapid systematic review of current scientific literature to identify and consolidate evidence of ICH in COVID-19 patients.
Methods
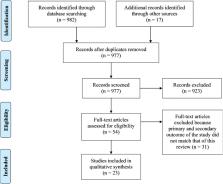
A systematic search of literature was conducted between November 1, 2019, and August 14, 2020, on PubMed and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) to identify eligible studies.
Results
A total of 23 studies describing ICH in 148 COVID-19 patients were included. The pooled incidence of ICH in COVID-19 patients was 0.7% (95% CI 0.5–0.9), with low levels of inter-study heterogeneity observed ( I 2 = 33.6%, Cochran’s Q = 12.05, p = 0.149). Most of the patients were elderly male patients (65.8%) with comorbidities, the most common being systemic hypertension (54%). Hemorrhage involving multiple cranial compartments was reported in 9.5% of cases. Single compartments were involved in the rest, with intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH) being the most common variety (62.6%) and intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) the least common (1.4%). Half of these patients were on some form of anticoagulation. Overall, the mortality rate in the COVID-19 patients with ICH was about 48.6%.
Related collections
Most cited references38
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
