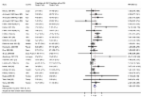
Background Multiple studies of tuberculosis treatment have indicated that patients with diabetes mellitus may experience poor outcomes. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to quantitatively summarize evidence for the impact of diabetes on tuberculosis outcomes. Methods We searched PubMed, EMBASE and the World Health Organization Regional Indexes from 1 January 1980 to 31 December 2010 and references of relevant articles for reports of observational studies that included people with diabetes treated for tuberculosis. We reviewed the full text of 742 papers and included 33 studies of which 9 reported culture conversion at two to three months, 12 reported the combined outcome of failure and death, 23 reported death, 4 reported death adjusted for age and other potential confounding factors, 5 reported relapse, and 4 reported drug resistant recurrent tuberculosis. Results Diabetes is associated with an increased risk of failure and death during tuberculosis treatment. Patients with diabetes have a risk ratio (RR) for the combined outcome of failure and death of 1.69 (95% CI, 1.36 to 2.12). The RR of death during tuberculosis treatment among the 23 unadjusted studies is 1.89 (95% CI, 1.52 to 2.36), and this increased to an effect estimate of 4.95 (95% CI, 2.69 to 9.10) among the 4 studies that adjusted for age and other potential confounding factors. Diabetes is also associated with an increased risk of relapse (RR, 3.89; 95% CI, 2.43 to 6.23). We did not find evidence for an increased risk of tuberculosis recurrence with drug resistant strains among people with diabetes. The studies assessing sputum culture conversion after two to three months of tuberculosis therapy were heterogeneous with relative risks that ranged from 0.79 to 3.25. Conclusions Diabetes increases the risk of failure and death combined, death, and relapse among patients with tuberculosis. This study highlights a need for increased attention to treatment of tuberculosis in people with diabetes, which may include testing for suspected diabetes, improved glucose control, and increased clinical and therapeutic monitoring.