- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Reliability of the interRAI suite of assessment instruments: a 12-country study of an integrated health information system
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
A multi-domain suite of instruments has been developed by the interRAI research collaborative to support assessment and care planning in mental health, aged care and disability services. Each assessment instrument comprises items common to other instruments and specialized items exclusive to that instrument. This study examined the reliability of the items from five instruments supporting home care, long term care, mental health, palliative care and post-acute care.
Methods
Paired assessments on 783 individuals across 12 nations were completed within 72 hours of each other by trained assessors who were blinded to the others' assessment. Reliability was tested using weighted kappa coefficients.
Results
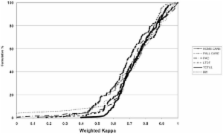
The overall kappa mean value for 161 items which are common to 2 or more instruments was 0.75. The kappa mean value for specialized items varied among instruments from 0.63 to 0.73. Over 60% of items scored greater than 0.70.
Conclusion
The vast majority of items exceeded standard cut-offs for acceptable reliability, with only modest variation among instruments. The overall performance of these instruments showed that the interRAI suite has substantial reliability according to conventional cut-offs for interpreting the kappa statistic. The results indicate that interRAI items retain reliability when used across care settings, paving the way for cross domain application of the instruments as part of an integrated health information system.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MDS Cognitive Performance Scale.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Comprehensive clinical assessment in community setting: applicability of the MDS-HC.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found