- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Microneedle-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Drug-Carrying Nanoparticles
Read this article at
Abstract
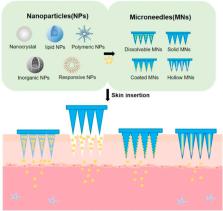
Drug-carrying nanoparticles have obtained great attention for disease treatments due to the fact that they can improve drug solubility, provide drug protection and prolong release duration, thus enhancing drug bioavailability and increasing therapeutic efficacy. Although nanoparticles containing drugs can be administered via different routes such as oral, intravenous and ocular, transdermal delivery of nanoparticles mediated by microneedles has attracted considerable interest due to the capability of circumventing enzymatic degradation caused by gastrointestinal track, and increasing patient compliance by reducing pain associated with hypodermic injection. In this review, we first introduce four types of nanoparticles that were used for drug delivery, and then summarize strategies that have been employed to facilitate delivery of drug-loaded nanoparticles via microneedles. Finally, we give a conclusion and provide our perspectives on the potential clinical translation of microneedle-facilitated nanoparticles delivery.
Related collections
Most cited references56
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found