- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Spatial, Temporal, and Habitat-Related Variation in Abundance of Pelagic Fishes in the Gulf of Mexico: Potential Implications of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill
Read this article at
Abstract
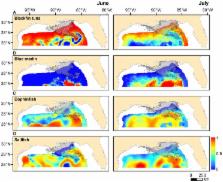
Time-series data collected over a four-year period were used to characterize patterns of abundance for pelagic fishes in the northern Gulf of Mexico (GoM) before (2007–2009) and after (2010) the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Four numerically dominant pelagic species (blackfin tuna, blue marlin, dolphinfish, and sailfish) were included in our assessment, and larval density of each species was lower in 2010 than any of the three years prior to the oil spill, although larval abundance in 2010 was often statistically similar to other years surveyed. To assess potential overlap between suitable habitat of pelagic fish larvae and surface oil, generalized additive models (GAMs) were developed to evaluate the influence of ocean conditions on the abundance of larvae from 2007–2009. Explanatory variables from GAMs were then linked to environmental data from 2010 to predict the probability of occurrence for each species. The spatial extent of surface oil overlapped with early life habitat of each species, possibly indicating that the availability of high quality habitat was affected by the DH oil spill. Shifts in the distribution of spawning adults is another factor known to influence the abundance of larvae, and the spatial occurrence of a model pelagic predator (blue marlin) was characterized over the same four-year period using electronic tags. The spatial extent of oil coincided with areas used by adult blue marlin from 2007–2009, and the occurrence of blue marlin in areas impacted by the DH oil spill was lower in 2010 relative to pre-spill years.
Related collections
Most cited references14
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Tracking apex marine predator movements in a dynamic ocean.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cascading effects of the loss of apex predatory sharks from a coastal ocean.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found