- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Patient engagement in research: a systematic review

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
A compelling ethical rationale supports patient engagement in healthcare research. It is also assumed that patient engagement will lead to research findings that are more pertinent to patients’ concerns and dilemmas. However; it is unclear how to best conduct this process. In this systematic review we aimed to answer 4 key questions: what are the best ways to identify patient representatives? How to engage them in designing and conducting research? What are the observed benefits of patient engagement? What are the harms and barriers of patient engagement?
Methods
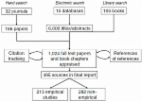
We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycInfo, Cochrane, EBSCO, CINAHL, SCOPUS, Web of Science, Business Search Premier, Academic Search Premier and Google Scholar. Included studies were published in English, of any size or design that described engaging patients or their surrogates in research design. We conducted an environmental scan of the grey literature and consulted with experts and patients. Data were analyzed using a non-quantitative, meta-narrative approach.
Results
We included 142 studies that described a spectrum of engagement. In general, engagement was feasible in most settings and most commonly done in the beginning of research (agenda setting and protocol development) and less commonly during the execution and translation of research. We found no comparative analytic studies to recommend a particular method. Patient engagement increased study enrollment rates and aided researchers in securing funding, designing study protocols and choosing relevant outcomes. The most commonly cited challenges were related to logistics (extra time and funding needed for engagement) and to an overarching worry of a tokenistic engagement.
Related collections
Most cited references16
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
RAMESES publication standards: meta-narrative reviews
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Evaluating meta-ethnography: a synthesis of qualitative research on lay experiences of diabetes and diabetes care.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found