- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Bacillus mojavensis, a Metal-Tolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium, Improves Growth, Photosynthetic Attributes, Gas Exchange Parameters, and Alkalo-Polyphenol Contents in Silver Nanoparticle (Ag-NP)-Treated Withania somnifera L. (Ashwagandha)
Read this article at
Abstract

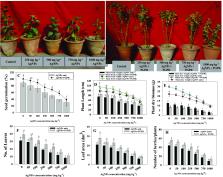
Discharge of nanoparticles (NPs) into aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems during manufacturing processes and from various commercial goods has become a significant ecotoxicological concern. After reaching soil systems, NPs cause deleterious effects on soil fertility, microbial activity, and crop productivity. Taking into consideration the medicinal importance of Withania somnifera (L.) (ashwagandha), the present study assessed the potential hazards of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) and the toxicity amelioration by a metal-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium (PGPR). Bacillus mojavensis BZ-13 (NCBI accession number MZ950923) recovered from metal-polluted rhizosphere soil, tolerated an exceptionally high level of Ag-NPs. The growth-regulating substances synthesized by B. mojavensis were increased with increasing concentrations (0–1000 μg mL –1) of Ag-NPs. Also, strain BZ-13 had the ability to form biofilm, produce alginate and exopolysaccharides (EPSs), as well maintain swimming and swarming motilities in the presence of Ag-NPs. Soil application of varying concentrations of Ag-NPs resulted in a dose-related reduction in growth and biochemical features of ashwagandha. In contrast, following soil inoculation, B. mojavensis relieved the Ag-NPs-induced phytotoxicity and improved plant productivity. Root, shoot length, dry biomass, and leaf area increased by 13, 17, 37, 25%, respectively, when B. mojavensis was applied with 25 mg/kg Ag-NPs when compared to noninoculated controls. Furthermore, the soil plant analysis development (SPAD) index, photosystem efficiency (Fv/Fm), PS II quantum yield (FPS II), photochemical quenching (qP), non-photochemical quenching (NpQ), and total chlorophyll and carotenoid content of BZ-13-inoculated plants in the presence of 25 mg Ag-NPs/kg increased by 33, 29, 41, 47, 35, 26, and 25%, respectively, when compared to noninoculated controls that were exposed to the same amounts of NPs. In addition, a significant ( p ≤ 0.05) increase in 48, 18, 21, and 19% in withaferin-A (alkaloids), flavonoids, phenols, and tannin content, respectively, was recorded when plants were detached from bacterized and Ag-NP-treated plants. Leaf gas exchange parameters were also modulated in the case of inoculated plants. Furthermore, bacterial inoculation significantly decreased proline, lipid peroxidation, antioxidant enzymes, and Ag-NP’s absorption and build-up in phyto-organs. In conclusion, soil inoculation with B. mojavensis may possibly be used as an alternative to protect W. somnifera plants in soil contaminated with nanoparticles. Therefore, phytohormone and other biomolecule-synthesizing and NP-tolerant PGPR strains like B. mojavensis might serve as an agronomically significant and cost-effective remediation agent for augmenting the yield and productivity of medicinally important plants like ashwagandha raised in soil contaminated with nanoparticles in general and Ag-NPs in particular.
Related collections
Most cited references87
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found