- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Concordance of Chronotype Categorisations Based on Dim Light Melatonin Onset, the Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire, and the Munich Chronotype Questionnaire
Read this article at
Abstract
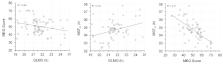
Chronotype reflects circadian timing and can be determined from biological markers (e.g., dim light melatonin onset; DLMO), or questionnaires (e.g., Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire; MEQ, or Munich Chronotype Questionnaire; MCTQ). The study’s aim was to quantify concordance between chronotype categorisations based on these measures. A total of 72 (36f) young, healthy adults completed the MEQ and MCTQ and provided saliva samples hourly in dim light during the evening in a laboratory. The corrected midpoint of sleep on free days (MSF sc) was derived from MCTQ, and tertile splits were used to define early, intermediate and late DLMO-CT, MEQ-CT and MSF sc-CT chronotype categories. DLMO correlated with MEQ score ( r = −0.25, p = 0.035) and MSF sc ( r = 0.32, p = 0.015). For early, intermediate and late DLMO-CT categories, mean(SD) DLMO were 20:25(0:46), 21:33(0:10) and 23:03(0:53). For early, intermediate and late MEQ-CT categories, mean(SD) MEQ scores were 60.5(5.3), 51.4(2.9) and 40.8 (5.0). For early, intermediate and late MSF sc-CT categories, mean(SD) MSF sc were 03:23(0:34), 04:37(0:12) and 05:55(0:48). Low concordance of categorisations between DLMO-CT and MEQ-CT (37%), and between DLMO-CT and MSF sc-CT (37%), suggests chronotype categorisations depend on the measure used. To enable valid comparisons with previous results and reduce the likelihood of misleading conclusions, researchers should select measures and statistical techniques appropriate to the construct of interest and research question.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A self-assessment questionnaire to determine morningness-eveningness in human circadian rhythms.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Life between Clocks: Daily Temporal Patterns of Human Chronotypes
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found