- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in Safety Event Reporting: PROSPER Consortium Guidance
Read this article at
Abstract
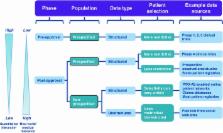
The Patient-Reported Outcomes Safety Event Reporting (PROSPER) Consortium was convened to improve safety reporting by better incorporating the perspective of the patient. PROSPER comprises industry, regulatory authority, academic, private sector and patient representatives who are interested in the area of patient-reported outcomes of adverse events (PRO-AEs). It has developed guidance on PRO-AE data, including the benefits of wider use and approaches for data capture and analysis. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) encompass the full range of self-reporting, rather than only patient reports collected by clinicians using validated instruments. In recent years, PROs have become increasingly important across the spectrum of healthcare and life sciences. Patient-centred models of care are integrating shared decision making and PROs at the point of care; comparative effectiveness research seeks to include patients as participatory stakeholders; and industry is expanding its involvement with patients and patient groups as part of the drug development process and safety monitoring. Additionally, recent pharmacovigilance legislation from regulatory authorities in the EU and the USA calls for the inclusion of patient-reported information in benefit–risk assessment of pharmaceutical products. For patients, technological advancements have made it easier to be an active participant in one’s healthcare. Simplified internet search capabilities, electronic and personal health records, digital mobile devices, and PRO-enabled patient online communities are just a few examples of tools that allow patients to gain increased knowledge about conditions, symptoms, treatment options and side effects. Despite these changes and increased attention on the perceived value of PROs, their full potential has yet to be realised in pharmacovigilance. Current safety reporting and risk assessment processes remain heavily dependent on healthcare professionals, though there are known limitations such as under-reporting and discordant perspectives between patient reports and clinician perceptions of adverse outcomes. PROSPER seeks to support the wider use of PRO-AEs. The scope of this guidance document, which was completed between July 2011 and March 2013, considered a host of domains related to PRO-AEs, including definitions and suitable taxonomies, the range of datasets that could be used, data collection mechanisms, and suitable analytical methodologies. PROSPER offers an innovative framework to differentiate patient populations. This framework considers populations that are prespecified (such as those in clinical trials, prospective observational studies and some registries) and non-prespecified populations (such as those in claims databases, PRO-enabled online patient networks, and social websites in general). While the main focus of this guidance is on post-approval PRO-AEs from both prespecified and non-prespecified population groups, PROSPER has also considered pre-approval, prespecified populations. The ultimate aim of this guidance is to ensure that the patient ‘voice’ and perspective feed appropriately into collection of safety data. The guidance also covers a minimum core dataset for use by industry or regulators to structure PRO-AEs (accessible in the online appendix) and how data, once collected, might be evaluated to better inform on the safe and effective use of medicinal products. Structured collection of such patient data can be considered both a means to an end (improving patient safety) as well as an end in itself (expressing the patient viewpoint). The members of the PROSPER Consortium therefore direct this PRO-AE guidance to multiple stakeholders in drug safety, including industry, regulators, prescribers and patients. The use of this document across the entirety of the drug development life cycle will help to better define the benefit–risk profile of new and existing medicines. Because of the clinical relevance of ‘real-world’ data, PROs have the potential to contribute important new knowledge about the benefits and risks of medicinal products, communicated through the voice of the patient.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Measurement of health status. Ascertaining the minimal clinically important difference.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found

