- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Ulcerative Colitis and Cytomegalovirus Infection: From A to Z
Read this article at
Abstract
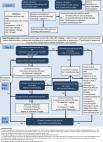
Despite multiple studies, the role of cytomegalovirus [CMV] infection in exacerbating the severity of inflammation in ulcerative colitis [UC], and its response to treatment, remain debatable. Additionally, the optimal diagnostic tests for CMV infection in the setting of UC relapse, and timing of antiviral treatment initiation, remain unclear. The challenge faced by gastroenterologists is to differentiate between an acute UC flare and true CMV colitis. It seems that the presence of CMV colitis, as defined by the presence of intranuclear or intracellular inclusion bodies on haematoxylin and eosin [H&E] staining and/or positive immunohistochemistry [IHC] assay on histology, is associated with more severe colitis. Patients with CMV infection and acute severe colitis are more resistant to treatment with corticosteroids than non-infected patients. This refractoriness to steroids is related to colonic tissue CMV viral load and number of inclusion bodies [high-grade CMV infection] which may have a pronounced effect on clinical outcomes and colectomy rates. Whereas many studies showed no effect for antiviral treatment on colectomy rates in CMV-infected UC patients, there was a significant difference in colectomy rates of patients with high-grade infection who received anti-viral therapy compared with those who did not receive treatment. It was therefore proposed that high-grade CMV disease indicates that the virus is acting as a pathogen, whereas in those with low-grade CMV disease, the severity of IBD itself is more likely to influence outcome. The different algorithms that have been put forward for the management of patients with UC and concomitant CMV infection are discussed.
Related collections
Most cited references90
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Third European Evidence-based Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Ulcerative Colitis. Part 1: Definitions, Diagnosis, Extra-intestinal Manifestations, Pregnancy, Cancer Surveillance, Surgery, and Ileo-anal Pouch Disorders.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
