- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A realist synthesis of the effect of social accountability interventions on health service providers’ and policymakers’ responsiveness
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
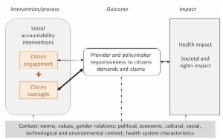
Accountability has center stage in the current post-Millennium Development Goals (MDG) debate. One of the effective strategies for building equitable health systems and providing quality health services is the strengthening of citizen-driven or social accountability processes. The monitoring of actions and decisions of policymakers and providers by citizens is regarded as a right in itself but also as an alternative to weak administrative accountability mechanisms, in particular in settings with poor governance. The effects of social accountability interventions are often based on assumptions and are difficult to evaluate because of their complex nature and context sensitivity. This study aims to review and assess the available evidence for the effect of social accountability interventions on policymakers’ and providers’ responsiveness in countries with medium to low levels of governance capacity and quality. For policymakers and practitioners engaged in health system strengthening, social accountability initiatives and rights-based approaches to health, the findings of this review may help when reflecting on the assumptions and theories of change behind their policies and interventions.
Methods/Design
Little is known about social accountability interventions, their outcomes and the circumstances under which they produce outcomes for particular groups or issues. In this study, social accountability interventions are conceptualized as complex social interventions for which a realist synthesis is considered the most appropriate method of systematic review. The synthesis is based on a preliminary program theory of social accountability that will be tested through an iterative process of primary study searches, data extraction, analysis and synthesis. Published and non-published (grey) quantitative and qualitative studies in English, French and Spanish will be included. Quality and validity will be enhanced by continuous peer review and team reflection among the reviewers.
Discussion
The authors believe the advantages of a realist synthesis for social accountability lie in the possibility of overcoming disciplinary or paradigmatic boundaries often found in public health and development. In addition, they argue that this approach fills the knowledge gap left by conventional synthesis or evaluation exercises of participatory programs. Finally, the authors describe the practical strategies adopted to address methodological challenges and validity.
Related collections
Most cited references5

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Individual determinants of research utilization by nurses: a systematic review update
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Embodied health movements: new approaches to social movements in health.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found