- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Two-Way Crossover Clinical Trial of ORADUR-Methylphenidate for Treating Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective: Methylphenidate (MPH) is efficacious in reducing symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but there are no data about the efficacy and safety of its new formulation (ORADUR ®-MPH extended release, ORADUR-MPH) in patients with ADHD, which is the study objective.
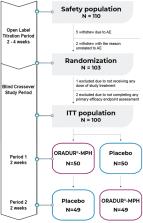
Method: This was a Phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-way crossover clinical trial. One hundred children and adolescents with a clinical diagnosis of ADHD (72.7% male) received at least one dose of ORADUR-MPH or a placebo during the 2-week treatment period of each phase. The primary efficacy measure was the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham-IV-teacher (SNAP-IV-T) form. Secondary efficacy measures included the SNAP-IV-parent form, the Clinical Global Impression: ADHD-Severity score, the Conner's Teacher's Rating Scale score, and the investigator's rating for 18 Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition ADHD symptoms. In addition, data related to vital signs, body weight, physical examination, laboratory testing, and adverse events (AEs) were also collected. All data were analyzed on an intent-to-treat basis.
Results: Without adjusting for differences in demographics and baseline measures, both treatment groups showed significant reductions in ADHD and oppositional defiant disorder symptoms after a 2-week treatment with greater effect sizes (Cohen's d) in the ORADUR-MPH group (Cohen's d ranging from −0.41 to −1.64; placebo, Cohen's d ranging from −0.26 to −1.18), except for oppositional symptoms, regardless of the informants. For the primary efficacy measure, ORADUR-MPH was significantly superior to the placebo, as evidenced by lower values for and greater reductions in the SNAP-IV-T scores at the endpoint (Cohen's d = −0.16, p = 0.005) and from baseline to the endpoint (Cohen's d = −0.19, p = 0.006), respectively. There were no serious AEs during the clinical study period. The most frequently observed AE was decreased appetite (49.1%). Most physical and laboratory test variables remained within the normal range.
Conclusions: Once-daily ORADUR-MPH is an effective, well-tolerable, and safe treatment for children and adolescents with ADHD. ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02450890.
Related collections
Most cited references101
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: a practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found