- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Simultaneous all-optical manipulation and recording of neural circuit activity with cellular resolution in vivo
Abstract
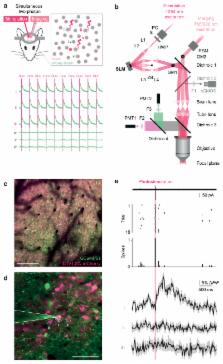
We describe an all-optical strategy for simultaneously manipulating and recording the activity of multiple neurons with cellular resolution in vivo. Concurrent two-photon optogenetic activation and calcium imaging is enabled by coexpression of a red-shifted opsin and a genetically encoded calcium indicator. A spatial light modulator allows tens of user-selected neurons to be targeted for spatiotemporally precise optogenetic activation, while simultaneous fast calcium imaging provides high-resolution network-wide readout of the manipulation with negligible optical crosstalk. Proof-of-principle experiments in mouse barrel cortex demonstrate interrogation of the same neuronal population during different behavioral states, and targeting of neuronal ensembles based on their functional signature. This approach extends the optogenetic toolkit beyond the specificity obtained with genetic or viral approaches, enabling high-throughput, flexible and long-term optical interrogation of functionally defined neural circuits with single-cell and single-spike resolution in the mammalian brain in vivo.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Neocortical excitation/inhibition balance in information processing and social dysfunction.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
