- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical Features and Outcomes of Peripheral Vascular Disease Patients Receiving Red Blood Cell Transfusions
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
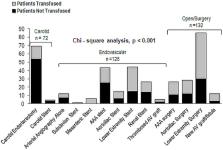
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) patients are commonly transfused with red blood cells (RBC) due to their inability to compensate for anemia and blood loss. Anemias, as well as allogeneic transfusions, have been demonstrated as independent risk factors for increased mortality and morbidity following cardiovascular procedures. The relationships between anemia, transfusion, and adverse outcomes in PVD patients remain unascertained and understudied.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was conducted to determine mortality at 30-day, one-year, and three-year markers among 330 randomly selected PVD patients. The clinical features of patients receiving transfusions were examined, and the mortality rates were compared between patients who received an RBC transfusion and those who did not. Cox regression analysis was employed to identify independent variables predicting mortality.
Results
Transfusions were found to have increased mortality rates over non-transfused patients at 30 days (6.1% vs. 1.8%, p = 0.05), one year (21.8% vs 12.1%, p = 0.02), and three years (41.2% vs. 23.0%, p = 0.001). Using a multivariate regression model, it was determined that the transfusion itself was not a significant cause of this decrease in survival, while the propensity to transfuse was a predictor for both short (30 days, 36.73 [1.85-728.06], p = 0.04) and long-term mortality (one year (8.83 [2.62-29.77], p < 0.001; three years (7.07 [1.46-8.07], p <0.01). Anti-coagulation therapy using intravenous (IV) heparin and the chronic comorbidities of coronary artery disease and diabetes mellitus were also robust independent predictors of decreased survival.
Conclusion
This study was able to find an association between RBC transfusion and reduction in short-term (three months) and long-term (three years) survival. Those requiring IV heparin during the hospital stay were at an increased risk of requiring blood transfusion, and patients receiving IV heparin were also found to have a significant increase in mortality rates.
Related collections
Most cited references18
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Effect of anaemia and cardiovascular disease on surgical mortality and morbidity.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Transfusion-related acute lung injury: definition and review.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found