- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Updated Global Burden of Cholera in Endemic Countries
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The global burden of cholera is largely unknown because the majority of cases are not reported. The low reporting can be attributed to limited capacity of epidemiological surveillance and laboratories, as well as social, political, and economic disincentives for reporting. We previously estimated 2.8 million cases and 91,000 deaths annually due to cholera in 51 endemic countries. A major limitation in our previous estimate was that the endemic and non-endemic countries were defined based on the countries’ reported cholera cases. We overcame the limitation with the use of a spatial modelling technique in defining endemic countries, and accordingly updated the estimates of the global burden of cholera.
Methods/Principal Findings
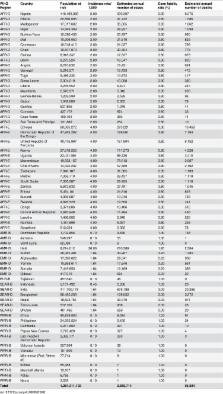
Countries were classified as cholera endemic, cholera non-endemic, or cholera-free based on whether a spatial regression model predicted an incidence rate over a certain threshold in at least three of five years (2008-2012). The at-risk populations were calculated for each country based on the percent of the country without sustainable access to improved sanitation facilities. Incidence rates from population-based published studies were used to calculate the estimated annual number of cases in endemic countries. The number of annual cholera deaths was calculated using inverse variance-weighted average case-fatality rate (CFRs) from literature-based CFR estimates. We found that approximately 1.3 billion people are at risk for cholera in endemic countries. An estimated 2.86 million cholera cases (uncertainty range: 1.3m-4.0m) occur annually in endemic countries. Among these cases, there are an estimated 95,000 deaths (uncertainty range: 21,000-143,000).
Author Summary
The global burden of cholera is largely unknown because the majority of cases are not reported. The low reporting can be attributed to limited capacity of epidemiological surveillance and laboratories, as well as social, political, and economic disincentives for reporting. We previously estimated 2.8 million cases and 91,000 deaths annually due to cholera in 51 endemic countries. A major limitation in our previous estimate was that the endemic and non-endemic countries were defined based on the countries’ reported cholera cases. If a country did not report cases even though the country had cholera, the country was classified as cholera free. This time we addressed this limitation by using a spatial modelling technique, which helped us define the cholera-endemic countries based on access to improved water and sanitation in the country as well as cholera incidence in neighboring countries. Our new estimate illustrates 2.9 million of cases and 95,000 deaths in 69 endemic countries, with the majority of the burden in Sub-Saharan Africa. The sustained high burden of cholera points to the necessity for integrated and improved control efforts, and these findings may help programmatic decision-making for controlling the disease in endemic countries.
Related collections
Most cited references9
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found