- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
An optimized and robust PEG precipitation method for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater
Read this article at
Abstract
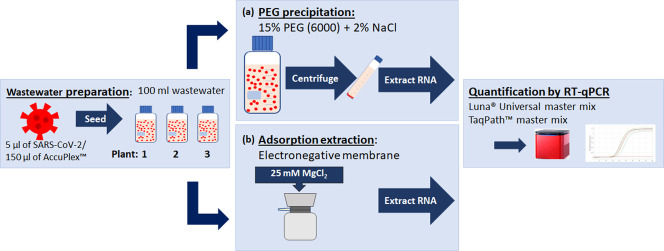
Wastewater-based epidemiology is currently being utilized to monitor the dissemination of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), on a population scale. The detection of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater is highly influenced by methodologies used for its isolation, concentration and RNA extraction. Although various viral concentration methods are currently employed, including polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation, adsorption-extraction, ultracentrifugation and ultrafiltration, to our knowledge, none of these methods have been standardized for use with a variety of wastewater matrices and/or different kits for RNA extraction and quantification. To address this, wastewater with different physical characteristics was seeded with gamma-irradiated SARS-CoV-2 and used to test the efficiency of PEG precipitation and adsorption-extraction to concentrate the virus from three physiochemically different wastewater samples, sourced from three distinct wastewater plants. Efficiency of viral concentration and RNA extraction was assessed by reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and the recovery yields calculated. As co-purification of inhibitors can be problematic for subsequent detection, two commonly used commercial master mixes were assessed for their sensitivity and efficiency to detect two SARS-CoV-2 target nucleocapsid (N) gene sequences. Recovery rates varied greatly between wastewater matrices and concentration methods, with the highest and most reproducible recovery rates (46.6–56.7%) observed when SARS-CoV-2 was precipitated with PEG and detected by the Luna® Universal master mix. The adsorption-extraction method was less effective (0–21.7%). This study demonstrates that PEG precipitation is the more robust method, which translates well to varying wastewater matrices, producing consistent and reproducible recovery rates. Furthermore, it is compatible with different kits for RNA extraction and quantitation.
Graphical abstract
Related collections
Most cited references45
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found