- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Telehealth voice assessment by speech language pathologists during a global pandemic using principles of a primary contact model: an observational cohort study protocol
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
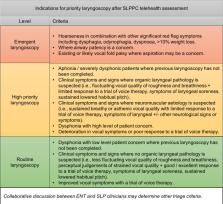
SARS-CoV-2, a highly contagious severe acute respiratory syndrome, has spread to most countries in the world and resulted in a change to practice patterns for the assessment and diagnosis of people with voice disorders. Many services are transitioning to telehealth models to maintain physical distancing measures and conserve personal protective equipment used by healthcare workers during laryngoscopy examinations. The speech–language pathology primary contact (SLPPC) assessment for patients referred to ear, nose and throat (ENT) services in Australia has been shown to reduce waiting times for assessment while streamlining access to ENT assessment and allied health practitioner treatment pathways.
Methods and analysis
A prospective observational cohort study will see patients in a newly developed telehealth model which uses the principles from a usual care SLPPC assessment protocol. Participants will be offered an initial telehealth assessment (speech–language pathology primary contact telehealth (SLPPC-T)) prior to being prioritised for a face-to-face laryngoscopy assessment to complete the diagnostic process. The telehealth assessment will collect sociodemographic information, personal and family medical history, key symptoms, onset and variability of symptoms, red-flag signs or symptoms for laryngeal malignancy, and clinical voice assessment data for auditory–perceptual and acoustic analysis. The study outcomes include (1) association of signs, symptoms and specific voice measures collected during SLPPC-T with voice disorder classification provided after laryngoscopy; (2) degree of concordance between voice disorder classification after SLPPC-T and after laryngoscopy; (3) health service and patient-related costs and health outcomes of the SLPPC-T; (4) patient and stakeholder views and beliefs about the SLPPC-T process.
Ethics and dissemination
Ethical approval has been granted prior to commencement of the study enrolment by the Gold Coast Hospital and Health Service Human Research Ethics Committee (reference number HREC/2020/QGC/62832). Results will be shared through the publication of articles in peer-reviewed medical journals and presentation at national and international scientific meetings.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found